 Mars-Bench :
Mars-Bench :
A Benchmark for Evaluating Foundation Models for
Mars Science Tasks
 Mars-Bench :
Mars-Bench :
A Benchmark for Evaluating Foundation Models for
Mars Science Tasks
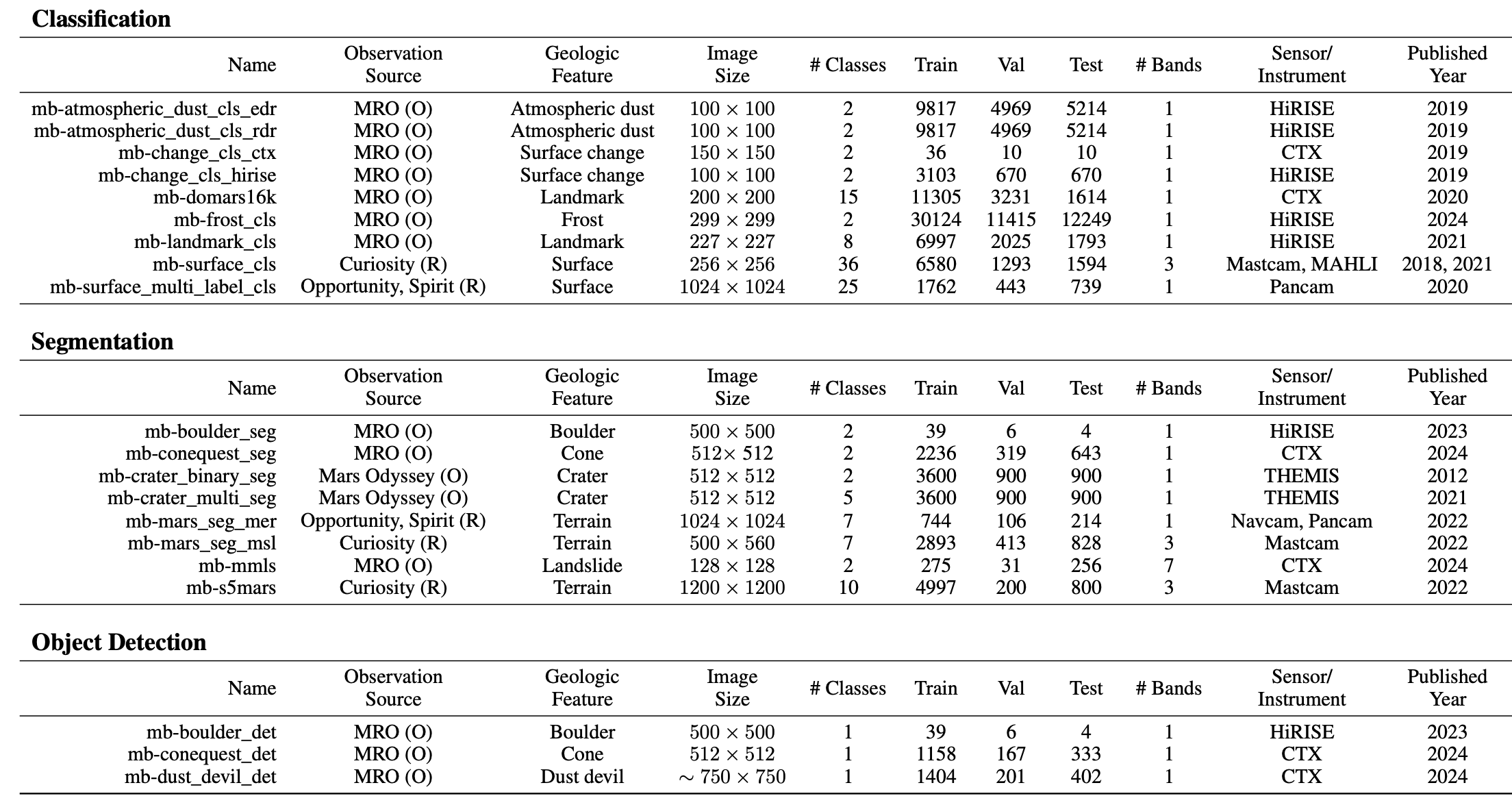
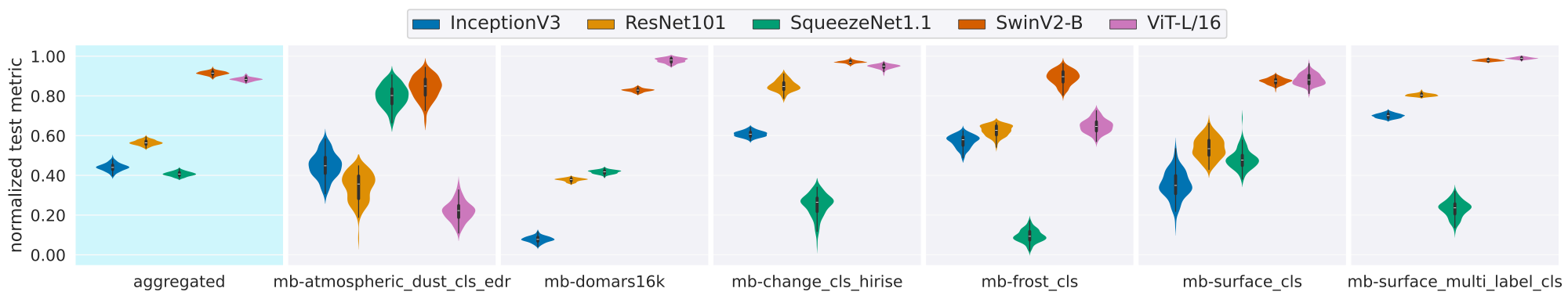
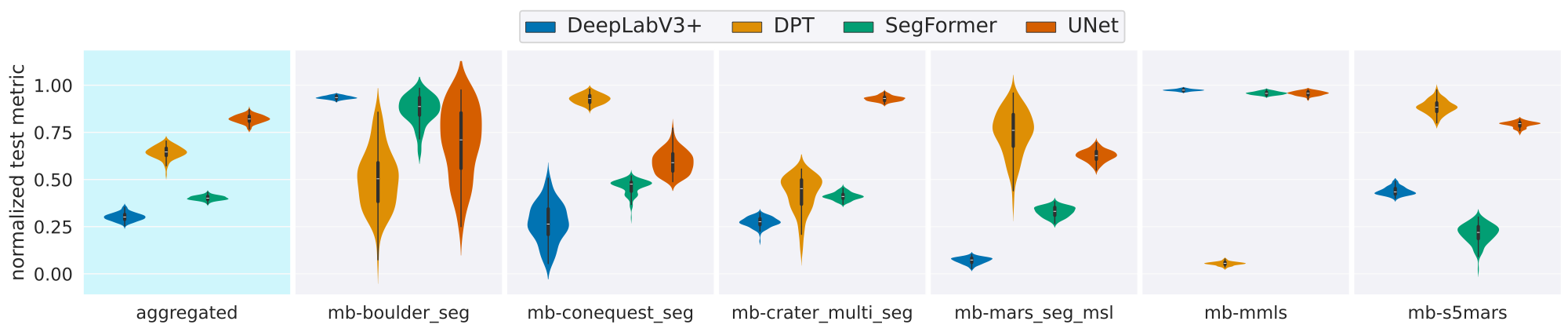
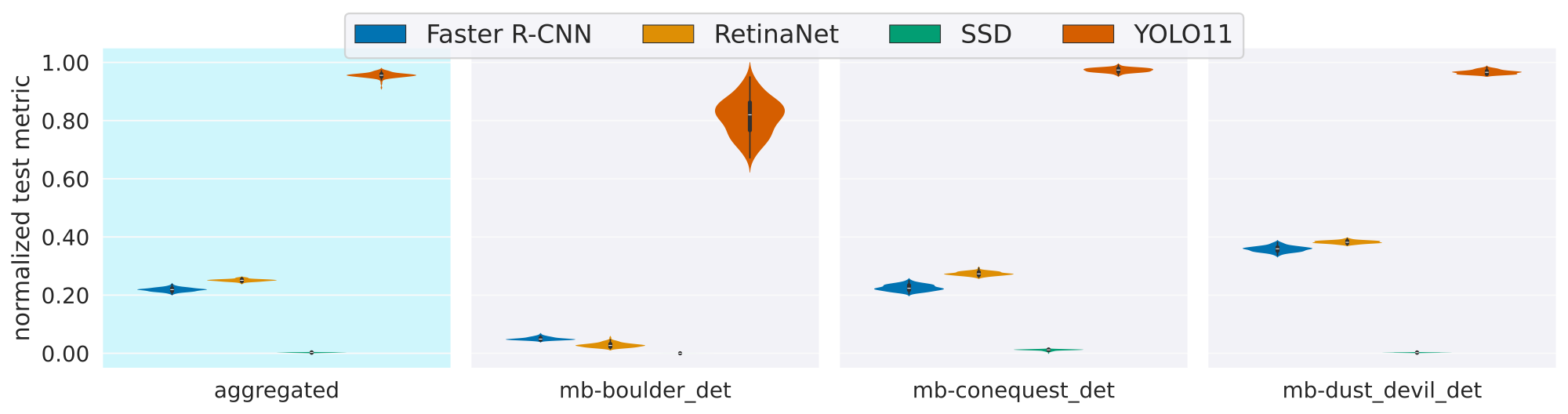
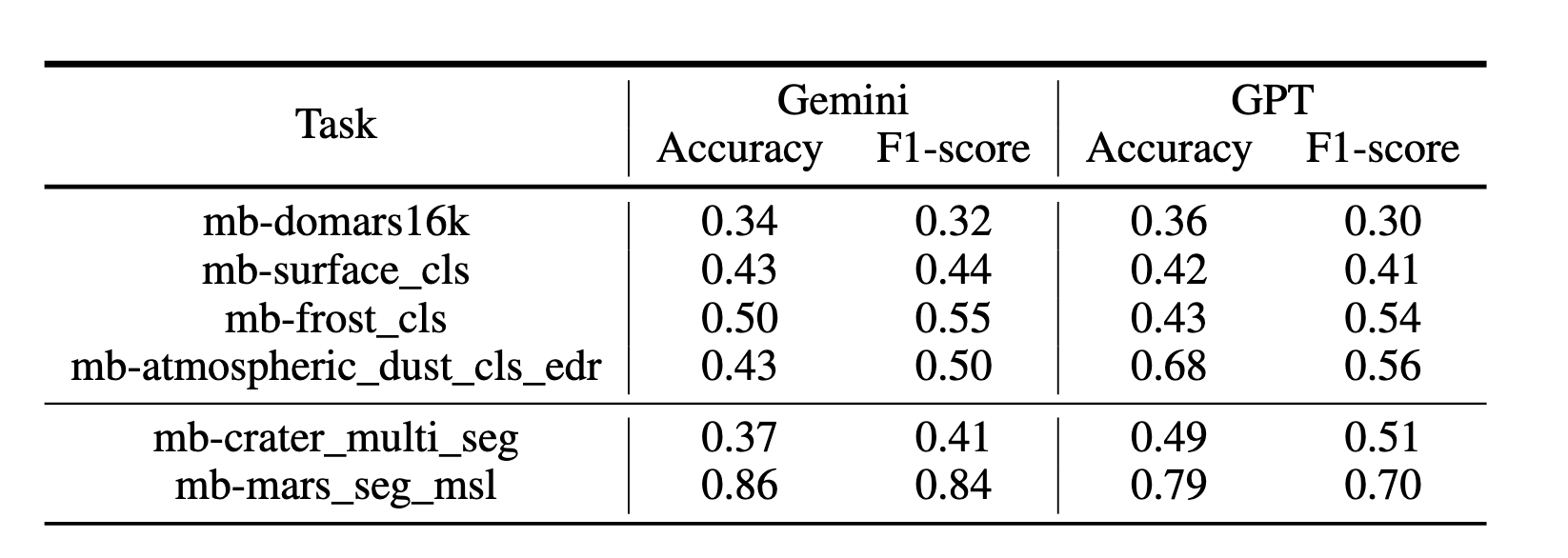
Foundation models have enabled rapid progress across many specialized domains by leveraging large-scale pre-training on unlabeled data, demonstrating strong generalization to a variety of downstream tasks. While such models have gained significant attention in fields like Earth Observation, their application to Mars science remains limited. A key enabler of progress in other domains has been the availability of standardized benchmarks that support systematic evaluation. In contrast, Mars science lacks such benchmarks and standardized evaluation frameworks, which have limited progress toward developing foundation models for Martian tasks. To address this gap, we introduce Mars-Bench, the first benchmark designed to systematically evaluate models across a broad range of Mars-related tasks using both orbital and surface imagery. Mars-Bench comprises 20 datasets spanning classification, segmentation, and object detection, focused on key geologic features such as craters, cones, boulders, and frost. We provide standardized, ready- to-use datasets and baseline evaluations using models pre-trained on natural images, Earth satellite data, and state-of-the-art vision-language models. Results from all analyses suggest that Mars-specific foundation models may offer advantages over general-domain counterparts, motivating further exploration of domain-adapted pre- training. Mars-Bench aims to establish a standardized foundation for developing and comparing machine learning models for Mars science.
@inproceedings{purohit2025marsbench,
title={Mars-Bench: A Benchmark for Evaluating Foundation Models for Mars Science Tasks},
author={Mirali Purohit and Bimal Gajera and Vatsal Malaviya and Irish Mehta and Kunal Sunil Kasodekar and Jacob Adler and Steven Lu and Umaa Rebbapragada and Hannah Kerner},
booktitle={The Thirty-ninth Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems Datasets and Benchmarks Track},
year={2025},
url={https://arxiv.org/pdf/2510.24010}
}